Theme IX: Essential oils
Terpenes
Terpenes. Definition and constitution. Terpene chemistry. Classification. Monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes, Hemiterpenes, Sesterterpenes, tetraterpenes, Polyterpenes. Geraniol, Citral, Limonene.
The terpenes are generally complex hydrocarbons CnH2n-4, from the isoprene series, which are made of two double bonds and linked by organic chains, form a group of compounds with own characteristics that determine the range of therapeutic effects present in plants containing them.
They are found in essential oils of plants. Their structures are related to the cymene (para-methyl isopropylbenzene) by forming a molecule derived from the condensation of two isoprene.
Classification of terpenes
The terpenes are classified by the number of isoprene contained and can appear in the following configurations:
- Three double bonds and acyclic
- Two double bonds and monocyclic
- A double bond and bicyclic
Hemiterpenes
Consist of a simple unit of isoprene. The isoprene itself is considered the only hemiterpene, but oxygen-containing derivatives such as isovaleric acid and prenol are hemiterpenoides.
Monoterpenes
Consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpene alcohol is also known as geraniol, the geranyl prefix indicates two isoprene units.
Sesquiterpenes
Consist of three isoprene units and have the molecular formula C15H24. Sesquiterpene alcohol is also known as farnesol, the farnesyl prefix indicates three isoprene units.
Diterpenes
They are composed of four isoprene units having the molecular formula C20H32. Derive from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Examples of diterpenoids include cembrene and taxadiene. Diterpenes form the basis of important biological compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol.
Sesterterpenes
They are terpenes having 25 carbons and 5 units isoprene, are rare in comparison to other sizes.
Triterpenes
Consisting of 6 units, they have the molecular formula C30H48. The linear triterpene squalene is the major constituent of shark liver oil, is derived from the reductive bond of two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate. Squalene is processed biosynthetically to generate Ianosterol, the structural precursor for all steroids.
Tetraterpenes
They have eight isoprene units and the molecular formula C40H56. Tetraterpenes are biologically important; include acyclic lycopene, gamma-carotene monocyclic and bicyclic alpha-and beta-carotene.
Polyterpenes
They consist of long chains of many isoprene units. Natural rubber is made of polyisoprene in which the double bond is cis. Some plants produce a type of polyisoprene with double trans bond, known as gutta-percha.
A typical example of the condensation of isoprene is the limonene which is a dimer and is classified as a monoterpene.

If in this condensation the chain stays opened are formed the olefinic terpenes, as geraniol and citral.
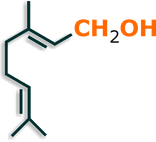

The number of terpenes and their derivatives is very large due to the position of double bonds, the possibility of oxygenated derivatives and carbon feature from the isopropyl group which can bind to another carbon atom of the hexagonal ring, forming another closed chain: bicyclic terpenes .
Thus there exist a variety of terpenoids formations with different structural characteristics.
From the terpenes are formed a variety of organic compounds derived from oxidation reactions, ring formation, substitution of atoms; which characterized them and give rise to the classification of acyclic and cyclic terpenes (mono, di-and tricyclic)
Besides the therapeutic effects provided by the terpenes to the plants containing them, essential oils have industrial significance in the manufacture of paints and varnishes.
Some vitamins, such as the derived from carotenoids are chains of tetraterpene characterized by the color of the vegetables containing them. Carotenoids are substances widespread in nature and are compounds similar to carotene.
See also
Monocyclic terpenes. Menthol - Limonene - thymol
Bicyclic terpenes. Camphor - borneol - pinene
Higher terpenes. Farnesol - beta carotene
Terpenes. Definition and constitution. Terpene chemistry. Classification. Monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes, Hemiterpenes, Sesterterpenes, tetraterpenes, Polyterpenes. Geraniol, Citral, Limonene.

 Pharmacognosy´s topics - Medicinal plants
Pharmacognosy´s topics - Medicinal plants


Write a comment